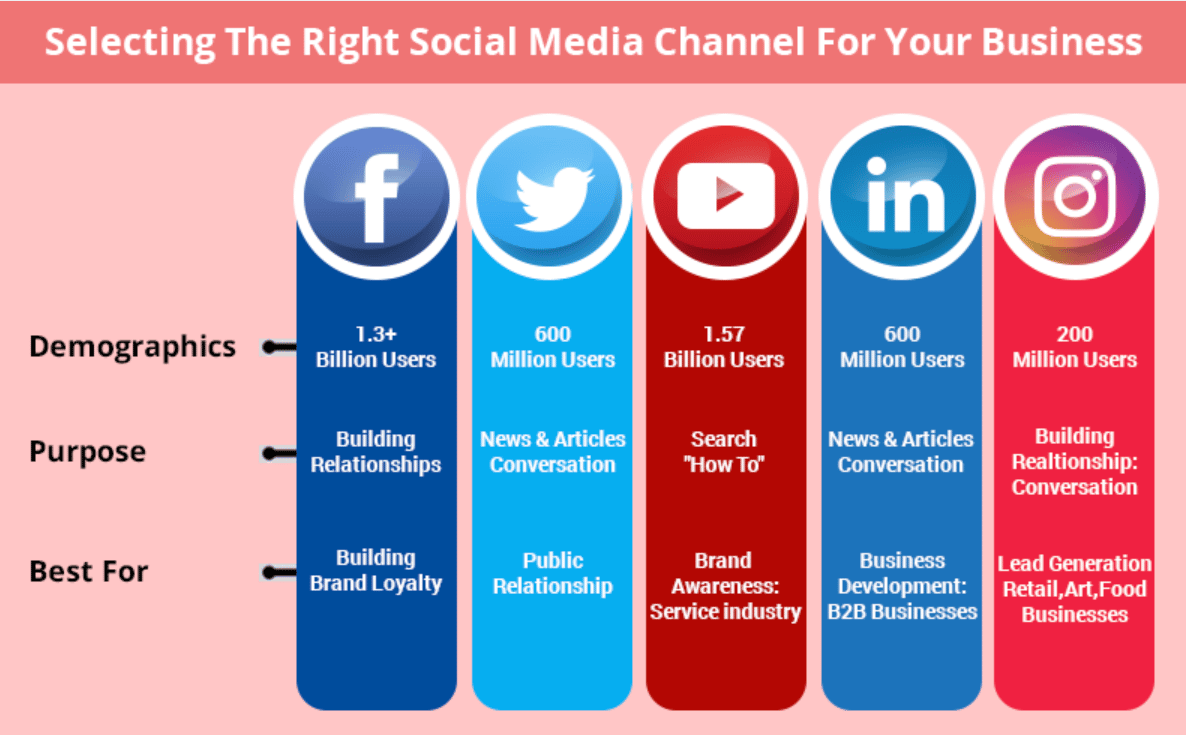
A well-crafted business plan is crucial for any business, whether you’re a startup seeking funding or an established company looking to grow. A business plan serves as a roadmap, guiding you through each stage of starting, managing, and scaling your venture. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll talk about how to write a business plan the process of creating a compelling plan that will help you achieve your goals.

What is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a strategic document that outlines your company’s mission, products or services, market analysis, organizational structure, marketing strategies, financial projections, and overall vision for growth. It’s a blueprint that communicates your business’s value proposition, target market, competitive advantages, and strategies for success.
Why Write a Business Plan?
Writing a business plan offers numerous benefits, including:
1. Clarifying Your Vision and Goals
The process of creating a business plan forces you to think critically about your business idea, define your objectives, and develop a roadmap for achieving them.
2. Securing Funding
Lenders and investors often require a detailed business plan to evaluate the feasibility of your venture and the potential return on their investment.
3. Identifying Strengths, Weaknesses, and Opportunities
Conducting market research and competitor analysis helps you understand your industry’s landscape, identify potential threats, and uncover opportunities for growth.
4. Attracting Talent and Partners
A well-crafted business plan can help you recruit top talent, solidify partnerships, and establish credibility with potential stakeholders.
5. Guiding Decision-Making
Your business plan serves as a reference point for making informed decisions, allocating resources, and measuring your progress against your goals.
Business Plan Formats
There are two main formats for business plans: traditional and lean startup. Choose the format that best suits your business needs and goals.
Traditional Business Plan Format
A traditional business plan is a comprehensive document that typically includes the following sections:
1. Executive Summary
2. Company Description
3. Market Analysis
4. Organization and Management
5. Service or Product Line
6. Marketing and Sales
7. Funding Request (if applicable)
8. Financial Projections
9. Appendix
Lean Startup Business Plan Format
The lean startup format is a more concise approach, focusing on the most critical elements of your business plan. It typically includes:
1. Key Partnerships
2. Key Activities
3. Key Resources
4. Value Proposition
5. Customer Relationships
6. Customer Segments
7. Channels
8. Cost Structure
9. Revenue Streams

Writing a Traditional Business Plan
If you choose to create a traditional business plan, here’s a step-by-step guide to help you through the process:
1. Executive Summary
Although this section appears first, it’s often written last. The executive summary is a concise overview of your business, including your mission statement, products or services, target market, competitive advantages, and financial highlights.
2. Company Description
In this section, provide detailed information about your company, including its legal structure, ownership, history, and mission. Highlight your team’s expertise, experience, and unique qualifications.
3. Market Analysis
Conduct thorough market research to understand your industry, target market, and competitors. Identify market trends, opportunities, and potential threats. Include a SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) analysis to evaluate your competitive position.
4. Organization and Management
Describe your company’s organizational structure, key personnel, and their roles and responsibilities. Include an organizational chart and resumes or bios of your management team.
5. Service or Product Line
Provide detailed descriptions of your products or services, including their features, benefits, pricing strategies, and intellectual property considerations.
6. Marketing and Sales
Outline your marketing and sales strategies, including your target customer segments, pricing, distribution channels, and promotional activities. Describe how you’ll acquire and retain customers.
7. Funding Request (if applicable)
If you’re seeking funding, clearly state the amount you need, the type of funding (debt or equity), and how you plan to use the funds. Explain your repayment or exit strategy for investors.
8. Financial Projections
Include detailed financial projections, such as income statements, balance sheets, cash flow statements, and break-even analyses. Provide realistic forecasts for the next three to five years, backed by solid assumptions and research.
9. Appendix
Include any supporting documents, such as contracts, licenses, permits, patents, or additional financial statements.
Writing a Lean Startup Business Plan
If you prefer a more concise approach, follow these steps to create a lean startup business plan:
1. Key Partnerships
Identify the key partners, suppliers, manufacturers, or subcontractors you’ll collaborate with to run your business.
2. Key Activities
List the critical activities that will give your business a competitive advantage, such as direct-to-consumer sales, technology integration, or leveraging the sharing economy.
3. Key Resources
Outline the essential resources your business needs to create value for customers, including staff, capital, intellectual property, or specialized equipment.
4. Value Proposition
Craft a clear and compelling statement that communicates the unique value your company brings to the market.
5. Customer Relationships
Describe how customers will interact with your business, whether it’s automated, personal, in-person, or online. Map out the entire customer experience.
6. Customer Segments
Define your target market with specific demographics, behaviors, and characteristics. Your business won’t be for everyone, so focus on the segments you can serve best.
7. Channels
List the most important channels you’ll use to communicate with and reach your customers, such as social media, email marketing, or physical retail locations.
8. Cost Structure
Determine whether your business will focus on reducing costs or maximizing value. List your most significant expenses based on your chosen strategy.
9. Revenue Streams
Explain how your company will generate revenue, whether through direct sales, membership fees, advertising, or other means. Identify all potential revenue streams.

Tips for Creating a Compelling Business Plan
1. Know Your Audience
Tailor your business plan to your intended audience, whether it’s lenders, investors, partners, or internal stakeholders. Adjust the level of detail and language accordingly.
2. Conduct Thorough Research
Gather reliable data and statistics to support your claims, assumptions, and projections. Conduct market research, competitor analysis, and industry trend analysis to ensure your plan is grounded in reality.
3. Keep It Concise and Clear
While comprehensive, your business plan should be concise, well-organized, and easy to read. Use clear language, avoid jargon, and consider using visual aids like charts and graphs to present complex information effectively.
4. Be Realistic and Credible
Avoid overly optimistic projections or unrealistic assumptions. Lenders and investors value honesty and transparency. Acknowledge potential risks and challenges, and outline contingency plans.
5. Regularly Update and Revisit
Your business plan is a living document that should evolve as your business grows and circumstances change. Regularly review and update your plan to ensure it remains relevant and aligned with your current goals and strategies.
By following these guidelines and best practices, you’ll be well-equipped to create a comprehensive and compelling business plan that will guide your business toward success.
Related Content
What must an entrepreneur assume when starting a business?
Things Entrepreneurs Need to Know
What is an Entrepreneurial Process
Resource
https://is.muni.cz/th/ze4kr/Final_edited_thesis.pdf
https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/38134523.pdf